Business Advisory

Business Valuation
At Modern Wealth, we offer business owners a powerful assessment strategy that reveals hidden value and unlocks growth potential. This process goes beyond financials to provide a comprehensive view of your company’s strengths, risks, and opportunities. With these insights, you gain clarity on what drives long-term value—empowering smarter decisions and sustainable success.
The result isn’t just a valuation—it’s a roadmap. Our structured framework helps you stabilize your foundation, optimize performance, and prepare for growth or transition. By reducing risk and improving efficiency, your business becomes more valuable—without relying solely on increased revenue.
This is about building more than a business—it’s about creating a transferable asset aligned with your life and legacy. With Modern Wealth, you move from uncertainty to confidence, with a clear path to growing your enterprise value and future financial freedom.

We leverage a value-focused assessment that delivers proprietary insights to guide smarter decisions. This includes a Quality Score that evaluates how well each area of your business functions and a Risk Score that identifies vulnerabilities—like inconsistent cash flow or compliance gaps—that can impact value or future transactions.
This approach helps uncover both hidden risks and untapped opportunities. It might reveal where leadership gaps could hinder growth or highlight how strong client relationships can be scaled for more significant returns. These insights are essential for building a resilient and growth-ready business.
This assessment evaluates strengths and areas for improvement, laying the groundwork for focused, strategic action. The result is a clearer path toward operational excellence, improved competitiveness, and enhanced enterprise value—so you’re not just running a business; you’re building an asset with lasting impact.

Value Optimization Plan
At Modern Wealth, we take business insights a step further with a customized Value Optimization Plan—an actionable roadmap designed to turn diagnostics into results. It provides clear strategies to reduce risk, overcome challenges, and unlock growth, all tailored to your unique business goals.
Whether scaling, stabilizing, or planning an exit, the plan aligns with your vision. Each recommendation is purpose-built to enhance value and confidently guide your next move. It’s a personalized framework that adapts to your priorities and keeps your business moving forward.
The plan is structured across three levels: stabilizing the foundation, strengthening operations, and preparing for long-term growth. This staged approach brings clarity and momentum to your strategy, helping you build a business that’s not just successful but truly valuable.

We help business owners enhance operational performance through a tailored Value Optimization Plan. This structured approach targets inefficiencies that reduce value—like outdated processes or weak financial controls—ensuring your business runs lean, focused, and profitably.
The plan provides clear strategies to build market readiness for those aiming to scale or attract investors. From developing a reliable sales pipeline to creating scalable systems and strengthening client retention, every recommendation supports long-term, sustainable growth.
Ultimately, this is about building a business that thrives now and is built to last. With the proper guidance and a clear roadmap, you gain a competitive edge that drives value today and sets the foundation for tomorrow.
Exit Plan
At Modern Wealth, exit planning is more than just a transaction—it’s about aligning your business, financial, and personal goals for a smooth, successful transition. Whether you’re considering a sale, family transfer, or buyout, early planning ensures you’re prepared and positioned to maximize value when the time comes.
By starting the process years in advance, you gain time to strengthen your business, reduce risks, and optimize performance. This proactive approach increases readiness, enhances outcomes, and helps you achieve financial peace of mind and personal fulfillment after the transition.
We also focus on your life beyond the business. From retirement and tax strategies to legacy planning or new ventures, our approach ensures that your exit supports your bigger picture. The result is a thoughtful transition that protects your wealth and powers your next chapter purposefully.
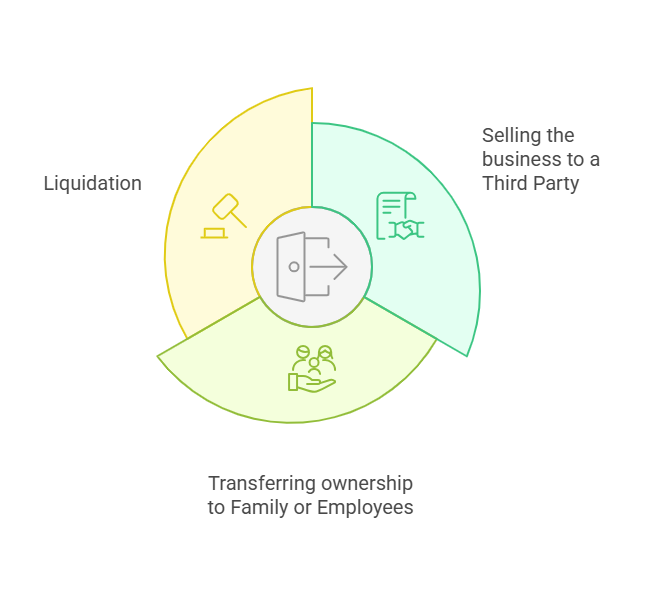
We help business owners prepare for a successful transition by ensuring that every detail of the exit process aligns with their goals. Thorough preparation is key, from enhancing market appeal to structuring the deal, and our guidance makes all the difference.
Not every exit looks the same. For some, transferring ownership to family or employees preserves legacy and culture, while strategies like buyouts or employee ownership plans reward loyalty and support continuity. With a clear and customized approach, we help navigate the complexities, from tax considerations to succession planning.
Sometimes, liquidation may be the most practical path when other options aren’t viable. Even then, thoughtful planning can protect value and minimize disruption. Whatever the scenario, we’re here to guide you through it so you exit on your terms, with clarity, confidence, and purpose.
Let's Chat
Join us for a complimentary 30-minute chat focused on your needs, goals, and vision. Enjoy a relaxed, no-pressure session to learn about our process and ask any questions. We’re here to listen, not to sell. Let’s discover what’s possible together!